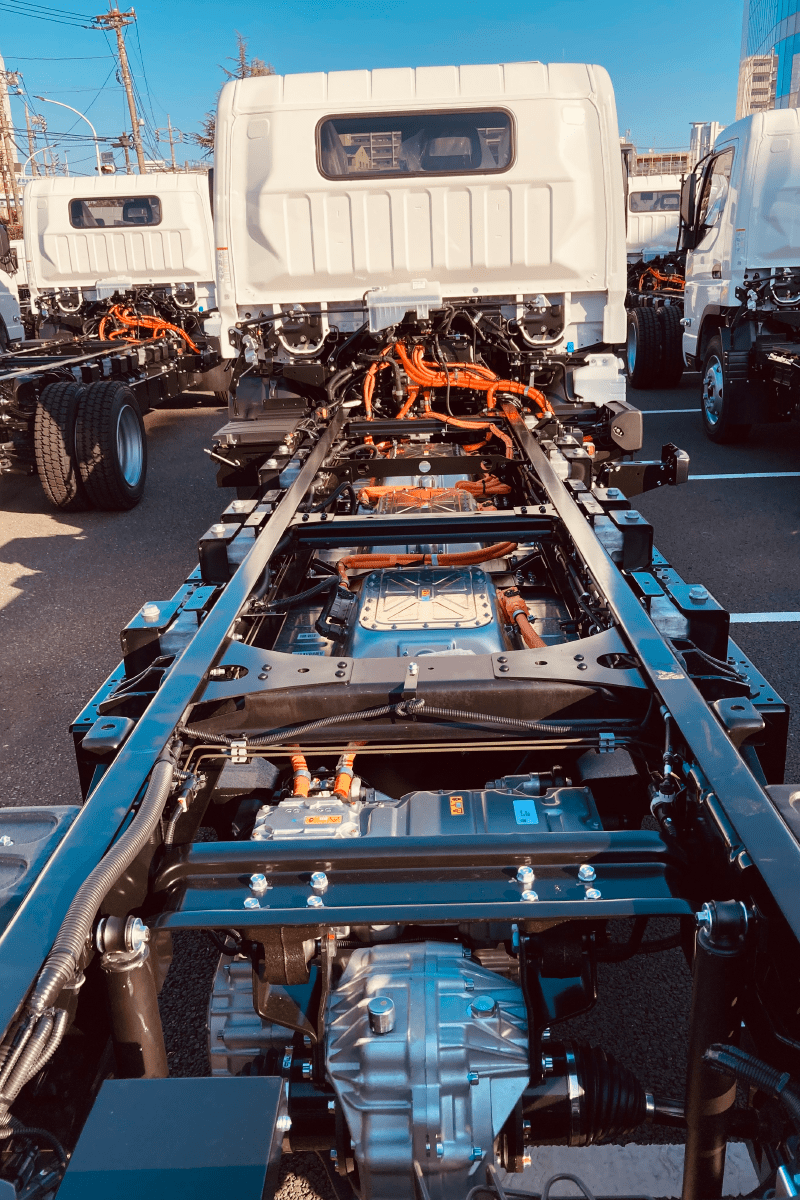
Electric vehicles are gaining greater acceptance, but they are encountering a public unaccustomed to the technology causing some customers to hesitate about making the switch due to concerns about battery, electrical, and overall electric vehicle high-voltage safety.
In this article, we will explore the key aspects of electric vehicle high-voltage drive system safety and the measures taken to protect both drivers and first responders. After reading, you should have a greater appreciation of electrical vehicle high-voltage safety.
When we talk about high-voltage in this article, we refer to the general classification according to ISO 6469-3 voltage class B, specifically to consider the low-voltage onboard system (12-48 volts) and high-voltage (> 60 volts DC and > 30 volts AC) separately, as other hazards prevail in the high-voltage range.
The Electric Vehicle Revolution
The electric vehicle revolution is well underway, driven by a global commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and decrease our dependence on fossil fuels. As a result, automakers are rapidly transitioning to powertrains, which rely on an electrical drive train.
High-Voltage Systems in Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles typically use lithium-ion batteries, which can operate at voltages ranging from 100 to 800 volts or even higher in some advanced models. Electrical systems operating in higher voltage ranges are necessary to become more efficient, which will lead to longer ranges, faster charging, and higher performance.
Battery technology is constantly evolving and will rapidly improve in the coming years. Likewise, the energy consumption of any vehicle component will decrease, and vehicles will continue to improve in efficiency.
As electric vehicles become more widespread, prices will also decrease. However, the higher the voltage, current, and stored energy, the greater the potential risks and impact associated with it. However, risks only arise in the event of serious faults or mishandling.
Handling of electric vehicles with an electric drive system
When handled properly, electric vehicles are much safer than vehicles with a conventional internal combustion engine. This is because electric vehicles have to meet much higher safety standards, such as functional safety (ISO 26262), which virtually rule out any danger to the people who use and handle them. However, it must be understood that electric vehicles harbor other risks and therefore, we must rethink how we handle them and become familiar with the issues associated with this technology.
Thermal Hazards:
A fault in a battery or a short circuit can result in thermal runaway. This can lead to the traction battery no longer being functional, to extreme heat development, or in the worst case, to a fire or electrolyte leakage.
In the case of a fire where electric vehicles or lithium-ion traction batteries are involved, different extinguishing techniques are required than those used for ordinary electrical fires. Water is still the best extinguishing agent since the focus is on cooling down the internal cell temperature, stopping the thermal runaway and the spread of the fire.
A lithium-ion traction battery that has undergone thermal runaway and developed a fire will continue to ignite due to the ongoing chemical reaction if the cell temperature is not lowered.
For its part, RIZON vehicles are equipped with lithium iron phosphate batteries, which are less prone to combustion and thermal runaway and are generally considered the safest type of lithium battery. The cathode material is also better for the environment.
First Responder Safety:
In the event of an accident, people involved including first responders, and firefighters need to be aware that they are handling an electric vehicle.
It should be noted that fires involving electric vehicles must be handled differently. Based on hazard analysis, a decision must then be made as to whether it makes sense to stop or prevent the thermal runaway or whether it is better to prevent the fire from spreading and allow it to burn down in a controlled manner.
Consideration must also be given to how to deal with electrolyte leaks or extremely contaminated extinguishing water. With regard to electrical hazards, the voltage source must be switched off safely to prevent electric shocks or other hazards.
Safety Measures in Electric Vehicles
Technical compliance organizations and automakers are committed to ensuring that the functions of the high-voltage drive system as such, as well as the functional safety and monitoring, are designed to the highest possible standards.
1. Vehicle Safety System:
Electric vehicles usually aren’t connected to earthed electrical systems when they aren’t connected to a charging station. For this reason, they are to be classified as unearthed systems (IT systems).
Electric vehicles protect the users and people who handle the vehicles from electric shocks via the IT system itself, the equipotential bonding, insulation of the overall system, additional system monitoring functions, etc.
In addition, orange cables and markings on the components of the electrical drive system and other protective measures indicate to the general public which components and connections carry high voltage.
2. Battery Management Systems:
Sophisticated battery management systems (BMS) monitor the state of the battery and can detect potential issues, such as thermal runaway, which can lead to fires. The BMS can take corrective actions to prevent hazardous situations.
3. Crash Safety:
RIZON trucks are designed with crash safety in mind. This includes structural components and emergency disconnect systems that can shut down the high-voltage system to prevent electrical hazards in the event of an accident.
4. First Responder Training:
RIZON is currently working on a program for emergency responders to receive specialized training to handle electric vehicle accidents. This training will include information about the location of high-voltage components, how to disable the high-voltage system, and how to extract occupants safely.
5. Hazard-free Maintenance:
Before a vehicle can be serviced, we have implemented a process that ensures that decommissioning for certain service activities can be realized safely and quickly.
This includes safety mechanisms and system requirements to put the system in a safe state (< 30 volts AC and < 60 volts DC). Even in the event of a system malfunction, it is not possible to come into contact with high voltage under normal conditions
6. Thermal Management:
Our vehicles are equipped with an advanced thermal management system that allows them to be used in both cold and warm regions without issue.
Active cooling of the battery regulates the temperature and reduces the likelihood of overheating or thermal events.
Suppose the internal temperature exceeds a certain threshold, e.g., during charging or driving, the charging current or power availability will be limited to safeguard the system and the battery. The active heating of the battery results in better performance, efficiency, and usable energy.
Government Regulations and Standards
To ensure uniform safety measures across the electric vehicle industry, governments and regulatory bodies have introduced standards and regulations. For example, the United Nations has established a Global Technical Regulation (GTR) for electric vehicle safety, addressing issues such as electrical safety, fire protection, and safety for the occupants and first responders.
In the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) have set specific safety standards for electric vehicles.
These regulations not only ensure the safety of electric vehicles but also promote innovation in the industry to enhance safety. OSHA also maintains certain programs for EV service technicians as well.
Charging Safety
Charging an electric vehicle is an essential aspect of EV ownership, and it comes with its own set of safety considerations:
1. Proper Equipment:
Use only approved charging equipment and cables. Low-quality or damaged cables can lead to electrical hazards. It must also be remembered that no extensions or cable drums should be used, as this can lead to thermal problems, short circuits, and even fires. Charging guns should be undamaged as they have safety mechanisms to prevent short circuits and accidental contact with live parts.
2. Domestic Charging:
If you charge an EV at your company or home, you need to ensure that the electrical installation has proper earthing and consists of cables that can handle high currents for several minutes and hours. The breakers must also be suitable for charging purposes. It is always advisable to have the electrical installation checked by a specialist beforehand.
3. Public Charging Stations:
When using public charging stations, make sure the equipment is in good condition and secure. Avoid using equipment with visible damage.
4. Overnight Charging:
One of the biggest advantages of electric vehicles is that they can be charged locally overnight without having to visit a gas station. Overnight charging is generally recommended to take advantage of lower electricity rates, but this should be done safely with approved chargers.
5. Environmental Considerations:
Care should always be taken to ensure that the charging inlet remains clean and dry. Foreign particles and moisture can lead to damage or charging interruptions.
Therefore, be especially mindful in bad weather or rough conditions. The penetration of moisture in winter can lead to mechanical damage after the water freezes. The charging flap should always be closed when the vehicle is not connected to a charging station. When the vehicle is connected to the charging station, the charging inlet is protected against environmental influences.
The Future of Electrical Vehicle High-voltage Safety
The safety of electric vehicles will continue to improve as technology evolves, and the industry matures. A big part of that has to do with the familiarity and understanding among vehicle users and handlers, which will increase over time as EVs become more widely implemented.
Innovations in materials, designs, and safety features will lead to even safer electric vehicles. Additionally, the ongoing development of autonomous vehicles may bring new safety advantages, as self-driving cars can be equipped with enhanced safety systems to minimize the risk of accidents.
As the electric vehicle market expands, it is crucial for consumers, manufacturers, and first responders to stay informed about safety best practices and the latest advancements in high-voltage safety technology in the automotive field.
Electric vehicle high-voltage safety is a paramount concern that can be solved through greater education and familiarity with the vehicles and their safe use. Over time, users will become more accustomed to handling EVs, their systems, and components.
Working Together
As electric vehicles become more common on our roads, it is essential to be aware of the unique safety considerations associated with electric vehicle high-voltage systems.
Automakers, governments, and regulatory bodies are working together to ensure the safety of electric vehicles through strict standards, training, and innovation. With continued efforts in research and development, electric vehicles will become even safer, helping to create a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future.
The electrification of the automotive industry is not only about reducing emissions but also about educating users on the safe use of EV technology to achieve greater familiarity. The safety of electric vehicles, their systems, and especially their traction batteries are a crucial part of this journey towards a more sustainable future.